Preface
The joint publication of the six ministries and commissions of the State Council has clearly promoted the rise of the LED industry. In recent years, with the rapid advancement of LED light efficiency and the significant cost reduction, the pace of LED entering the lighting field has obviously accelerated. The “LED Lighting Demonstration Project†project launched by the National Development and Reform Commission last year has made the enthusiasm of practitioners in this field unprecedentedly high. However, due to the general lack of knowledge and understanding of the standards in this field, companies and practitioners have caused LEDs. There are many common problems in the design of lighting products. If you do not seriously study and solve them, it will lead to more detours and waste a lot of resources. Careful analysis and study of these issues is an important task for the healthy development of this industry.
First, the main safety issues of road lamps
1. Unused tempered glass
According to the requirements of GB7000.5, road lamps, including tunnel lamps, should use tempered glass. The use of tempered glass not only requires the mechanical strength of the glass, but also the glass is broken. Normal glass is like the case of Figure 1. The glass fragments are large and many Sharp angles are easy to hurt when falling. If tempered glass is used, once the condition is broken, the tempered glass will break into many small particles with no obvious acute angle.
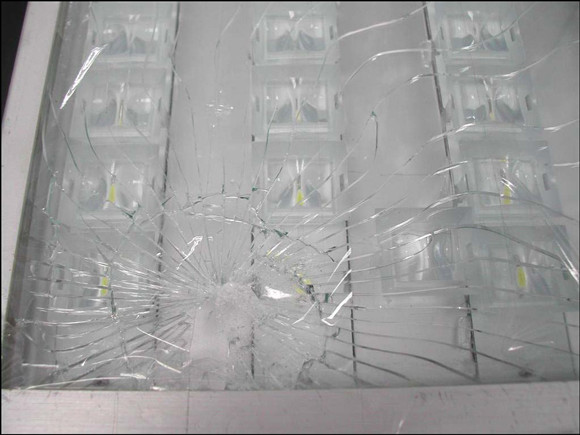

Figure 1: Glass shards after broken glass
2. The LED control unit is external, but the control unit does not have a separate mark.
The LED control unit is external and the control unit must be self-contained. With independent marking, it means that the relevant parts must meet the relevant requirements of the luminaire standard, such as: fixing device for external wires; protection against electric shock; temperature of mounting surface; IP (dustproof, waterproof) test, etc. It is only understood that IP (dustproof, waterproof) testing is required, so LED control devices that do not have a separate mark and are not tested for luminaire standards are not allowed to be external. A separately mounted control unit with a relatively complete marking is shown in Figure 3.

Figure 2: No stand-alone tag, just write IP67

Figure 3: Stand-alone control unit with a relatively complete mark
3. The external cable does not meet the standard requirements.
GB7000.5 Safety requirements for roads and street lighting The requirements for external conductors for road and street lighting are mainly based on the requirements of GB7000.1 Standard 5.2, “If the cable or cord provided by the luminaire manufacturer is connected to the power supply In terms of their mechanical and electrical properties, they shall comply with at least the provisions of GB5023 and GB5013, as shown in Table 5.1.
Table 5.1 - Non-removable flexible cable or cord
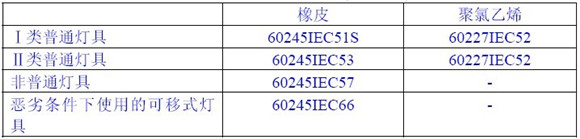
Note 1: When the power supply voltage is greater than 250V, it may be necessary to use a cord and a flexible cable with a voltage rating higher than the one specified in the above table.
In order to provide sufficient mechanical strength, the nominal cross-sectional area of ​​the conductor shall not be less than:
— ordinary lamps 0.75mm2
— Other lamps 1.0 mm2
If the luminaire is provided with a 10/16A socket, the nominal cross-sectional area of ​​the soft conductor should be no less than 1.5mm2.
According to the requirements of Table 5.1, LED road lamps are non-ordinary lamps, and cables of 60245IEC57 or higher should be used. Many companies simply do not know or understand the above standard requirements, so there are many requirements for the lead wires of road lamps that do not meet the mandatory standards.

Figure 4: Qualified external cable
4, the connector does not meet the dustproof and waterproof requirements of the whole lamp
Many of the connectors for road luminaires are directly exposed to open conditions, so the connectors need to meet the same IP protection requirements for road luminaires and maintain reliable electrical contact. The connectors that are not waterproof are shown in Figure 5. Many of these types of waterproof connectors are used in the IP44 string. Generally, IP65 and above are not available. The connectors that meet the IP protection requirements are shown in Figure 6. This connector can reach the IP66 rating.

Figure 5: Unqualified connector

Figure 6: Qualified connector
5. How does lightning protection surge circuit meet safety requirements?
Due to global warming, the probability of various harsh climates is increasing. Among them, lightning has great destructive power to outdoor lighting appliances, and there must be countermeasures.
China's power supply network is a YY-type zero-wire grounded 220V/380V polar power supply. Lightning is a broad-spectrum radio wave. After receiving the electromagnetic wave caused by lightning, the overhead line of the lighting grid will produce the phase line--the differential mode between the zero lines because of the difference between the phase line and the neutral-to-ground impedance. Surge voltage and phase line, neutral line - common mode surge voltage between ground (shell). For differential mode surges, the method of parallel varistor and/or network at the input can be effectively protected. This part of the circuit in Figure 7 is satisfactory, but the common mode lightning protection circuit in this part of the circuit is wireless. The common mode anti-circuit in the fast transmission network has also moved to the LED control device, which is obviously not in line with the safety standards of low-voltage electrical appliances. This has been in contact with international organizations and reached a consensus.
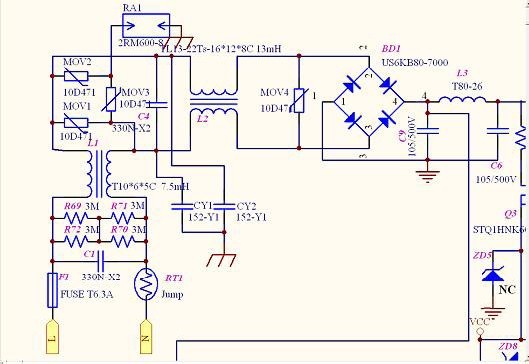
Figure 7: Defects of the most commonly used lightning surge circuits