While LED dimming is a new selling point in the consumer market, consumers are unaware that the performance of many LED lights may not be ideal, and the performance varies depending on the dimmer and circuit load used. Sometimes, when the LED light is installed in a room with a dimmer, the LED light will flicker and the brightness cannot be adjusted evenly.
The driver circuit of the LED lamp converts the AC input power into a low-voltage DC power supply and maintains a constant current, driving a high-brightness LED load to achieve a constant light output. In order to adjust the basic LED driver circuit through a bidirectional thyristor-based dimmer, additional components must be added to achieve stable dimmer operation and regulate the output current based on the dimmer phase angle.

Figure 1 Schematic diagram of a typical dimming circuit
The single-stage LED driver example circuit (Figure 2) replaces the resistive load representing the incandescent lamp in Figure 1. Although this circuit simulates a resistive load due to its high power factor during stable operation, its front end also includes the capacitors necessary for EMI filtering.
In addition, LED bulbs consume less than 25% of the equivalent incandescent lamps. As a result, the dimmer is primarily subjected to capacitive loads during the AC line half cycle before the TRIAC triggers.
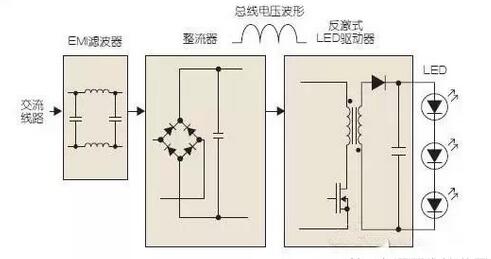
Figure 2 Basic LED driver circuit block diagram
The bidirectional trigger circuit shown in Figure 1 requires a resistive path to the neutral point if it is intended to operate as designed. If it is changed to a capacitive load, this circuit will not operate normally, and will lead to unstable triggering during periodic conversion, which is manifested by the blinking of the output light. The EMI filter in the dimmer and LED driver also causes ringing oscillations due to the high dv/dt at the start of the TRIAC.
From the above explanation, we can understand that when the amplitude of the oscillation reaches a certain level, the current will drop below the "hold current", so that the TRIAC is turned off, and the TRIAC cannot be turned on until the next line crosses zero. This condition is usually caused by the trigger circuit re-triggering the TRIAC, causing it to turn on and off multiple times in a single line half cycle. In addition to stressing components and possibly destroying dimmers or LED drivers, this can result in severe flicker and unpleasant noise conditions.
Qiuck deatail:
- Synchronization mechanism for multi-screen playing
- Powerful processing capability
- Comprehensive control plans
- Synchronous and asynchronous dual-mode
- Dual-Wi-Fi mode
Other Hardware Features
- 4 Ethernet ports, loading capacity of each port up to 2,300,000 pixels, with the maximum width of 4096 pixels and maximum height of 1920 pixels
- Wired Gigabit Ethernet
- Stereo audio output
- HDMI Loop
- HDMI input and auto full-screen display
- 2 USB ports allowing for USB playback
- Onboard light sensor connector allowing for automatic and scheduled brightness adjustment
Application:
Movie theaters, clubs, stages.
* Business Organizations:
Supermarket, large-scale shopping malls, star-rated hotels, travel agencies
* Financial Organizations:
Banks, insurance companies, post offices, hospital, schools
* Public Places:
Subway, airports, stations, parks, exhibition halls, stadiums, museums, commercial buildings, meeting rooms
* Entertainments:
Video processor,controller,video controller
Guangzhou Chengwen Photoelectric Technology co.,ltd , https://www.cwleddisplay.com