Describes ways to help the automotive lighting industry achieve optimal thermal management. We discussed the selection and measurement of LED thermal characteristics and the selection of the most appropriate LED for a particular application. Since temperature overheating can destabilize the LED system, we also discuss the thermal simulation of complex lighting systems such as headlights and taillights, and the use of synchronous computational fluid dynamics to design higher quality products faster and more Develop automotive lighting systems in an efficient and cost-effective way.
This article refers to the address: http://
According to McKinsey & Company's insights into the global lighting market, the automotive lighting market is currently approximately $18 billion (13 billion euros), accounting for approximately 20% of the entire lighting market and is expected to increase to $25 billion by 2020. (18 billion euros). With the development of LEDs, LEDs in automotive applications are expected to grow significantly over the next 10 years. According to an article published in November 2012 by LEDs Magazine, all lighting systems of Daimler's upcoming S-series Mercedes will use LEDs. From 2010 to 2020, the price of LEDs will be reduced to one-tenth of the current price, so LEDs will be more competitive than traditional light sources. Unlike traditional automotive lighting sources, LEDs are more sensitive to temperature, not just need A good understanding of the structure and characteristics of the LEDs used in the design requires an understanding of the entire thermal management system from the heat sink to the cooling fluid. With these skills, lighting designers can optimize their designs to ensure long-lasting LEDs, minimize transmission wavelength shifts, or minimize light output loss. They can also use LEDs as a light source more effectively and drive the full popularity of LEDs in the automotive industry.
The challenge of using LEDs in automotive lighting
As light source designs shift from incandescent to LED, traditional thermal management concepts are outdated and new ways of thinking are needed. About 83% of the energy of most incandescent lamps forms heat radiation, and about 12% forms heat loss, which does not face the problem of heat dissipation from the light source. LEDs mostly transfer heat loss through conduction (about 60-85%) and are very sensitive to thermal management. The 100 watt incandescent lamp has an electro-optic conversion efficiency of only about 5%, and the conversion efficiency of the LED can reach about 15-40%, and is still increasing.
The main thermal challenge for LEDs is to maintain high chroma stability and life expectancy. LEDs in the automotive industry need to be lifelong. LEDs are not only more efficient, but their higher visibility is also valuable and therefore safer. The Economic Commission for Europe (ECE) requires that all new cars be equipped with daytime running lights (DRL) from 2011 onwards. Because external lights such as headlights and taillights are almost completely sealed systems (except for small airflow inlets, outlets, and small openings for ordinary incandescent lamps), it is unrealistic to replace LEDs with a flaw. When multiple LEDs of the headlights or taillights fail, they can only be solved by replacing the entire lamp. Therefore, not only LEDs, but the entire luminaire design must have high reliability and quality, because replacing the entire headlights is expensive; if it is still under warranty, then the original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) and suppliers of the system will It costs a lot. Original supplier data sheets do not always provide the data needed to derive accurate and reliable simulation results from fluid or structural analysis; manufacturers do not often provide assurance or instructions for measurement data errors. Therefore, you will need to test and measure the characteristics of your vehicle before installing it to ensure the reliability of parts and materials.
Thermal characteristics
The thermal resistance (Rth) of an LED can affect the life, efficiency, and operation of multiple domains, as well as electrical, thermal, and optical performance (Figure 1). Like all other semiconductor device kits, the LED kit provides excellent characterization through thermal resistance for stable operation. The thermal resistance (Rth) value tells us how much the temperature rises when a unit heat source is applied to the device.
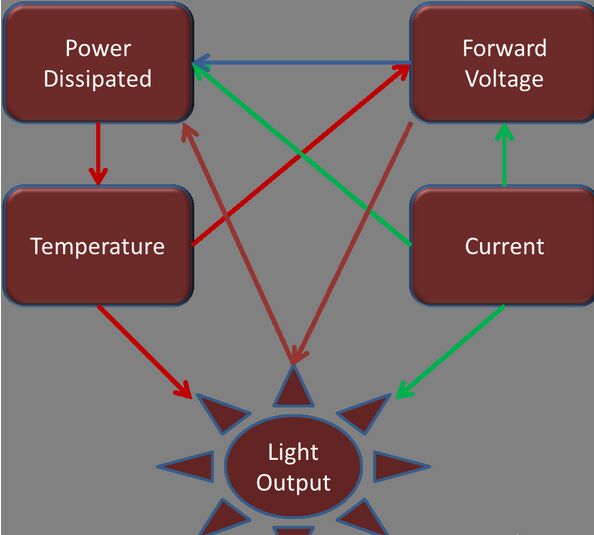
Figure 1: Thermal issues affect every aspect of the LED package.
The most basic method is to measure the temperature-dependent voltage of the component. The LED turns on or off from a stable state, and after a while, it reaches another stable state (hot/cold, and vice versa). Transient measurements are continuously performed during this process, providing a thermal transient response curve at very small measurement currents. With the help of the measured temperature difference and power difference (for switching components) (Figure 2), the structure function can be derived (Figure 3).
HuiZhou Superpower Technology Co.,Ltd. , https://www.spchargers.com