Luminous flux
Light metric derived from the effect of radiation on a standard luminosity observer.
The unit is lumens (lm), 1lm=1cd/1sr. For Ming Vision there are:

In the formula:
dΦe(λ)/dλ--the spectral distribution of the radiant flux;
ν(λ)--spectral light (visual) efficiency;
Km - The maximum value of the spectral (visual) performance of radiation in lumens per watt (lm/W). In the case of monochromatic radiation, the Km value under bright visual conditions is 683 lm/W (when λm = 555 nm).
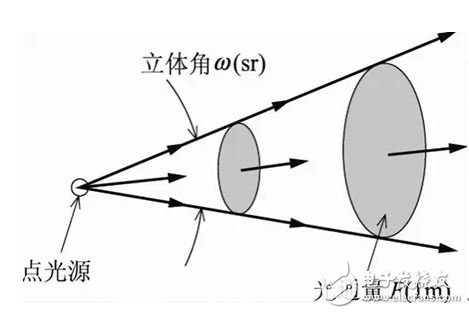
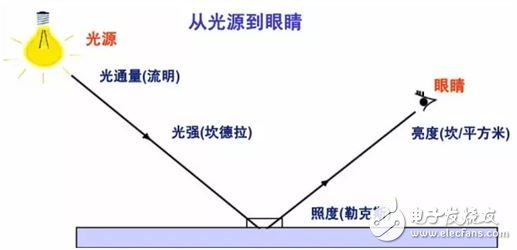
2. Luminous intensity
The luminous intensity of the illuminant in a given direction is the quotient of the luminous flux dΦ transmitted by the illuminant in the solid angle element dΩ in that direction divided by the solid angle element, that is, the luminous flux per unit solid angle.
The unit is Candela (cd), lcd = 1 lm / sr.
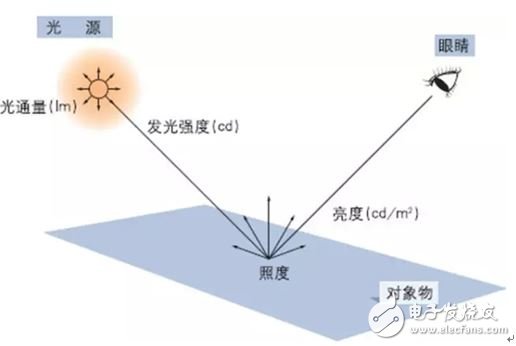
3. Brightness luminance
Luminance refers to a physical quantity in which the surface of the illuminant (reflector) is bright (reflective). The human eye observes the light source from one direction. The ratio of the light intensity in this direction to the area of ​​the light source "visible" by the human eye is defined as the brightness of the light source unit, that is, the luminous intensity per unit projected area.
The amount defined by the formula L = d2 Φ / (dA · cos θ · d Ω), the unit is candela per square meter (cd / m2).
In the formula:
dΦ--the luminous flux (lm) transmitted by a beam element at a given point and containing a solid angle dΩ in a given direction;
dA--including the beam cross-sectional area (m2) at a given point;
Θ—the angle between the normal of the beam section and the beam direction.
4. Illuminance illuminance
A physical quantity indicating the brightness of the illuminated surface. The illuminance at a point on the surface is defined as the ratio of the luminous flux incident on the bin on this point to the area of ​​the bin. In numerical terms, it is equal to the luminous flux projected over a unit area.
The quotient of the luminous flux dΦ incident on the bin containing the point divided by the bin area dA, in lux (lx), 1 lx = 1 lx/m2.
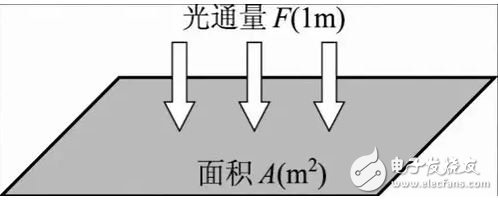
5. Average illumination average illuminance
Specifies the average of the illuminance at each point on the surface.
Average illuminance (Eav) = total luminous flux of the source (N*Ф) * utilization factor (CU) * maintenance factor (MF) / area (m2) (for indoor or stadium lighting calculations)
6. Maintain average illuminance maintained average illuminance
The average illuminance on the specified surface shall not be lower than this value. It is the average illuminance on a defined surface at the moment the luminaire must be maintained.
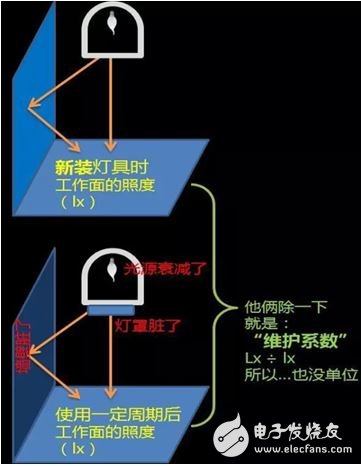
7. Maintenance factor maintenance factor
The ratio of the average illuminance or average brightness of the illuminating device on a given surface after a certain period of use, compared to the average illuminance or average brightness obtained on the same surface when the device is newly installed under the same conditions.
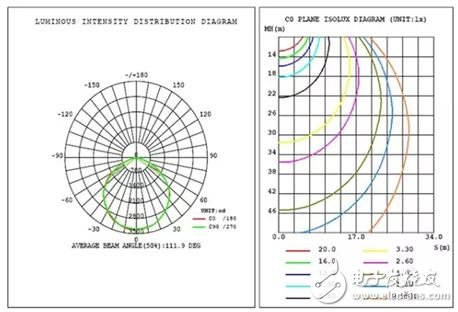
8. Light intensity distribution distribuTIon of luminous intensity
The curve or table is used to indicate the luminous intensity value of the light source or the luminaire in all directions of the space, also called light distribution.
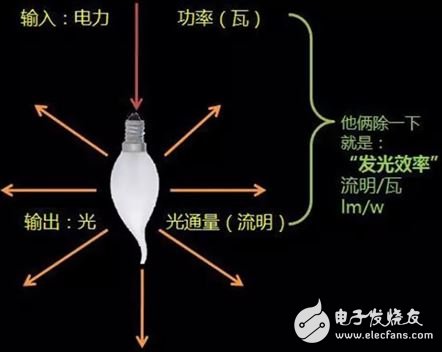
9. Luminous efficacy of a light source
The luminosity obtained by dividing the luminous flux emitted by the light source by the power of the light source is referred to as the luminous efficacy of the light source. The unit is lumens per watt (lm/W).
10. Luminaire efficiency luminaire efficiency
Under the specified conditions of use, the ratio of the total luminous flux emitted by the luminaire to the total luminous flux emitted by all sources within the luminaire, also known as the luminaire's optical output ratio.
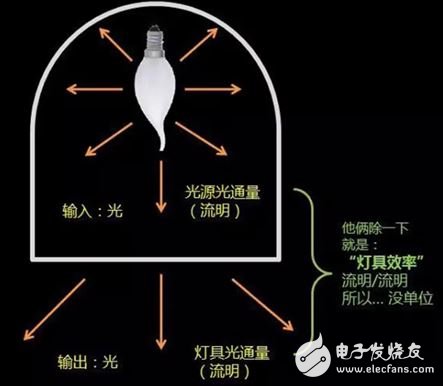
11. Luminaire efficacy
The ratio of the total luminous flux emitted by the luminaire to the power it inputs under the specified conditions of use. The unit is lumens per watt (lm/W).
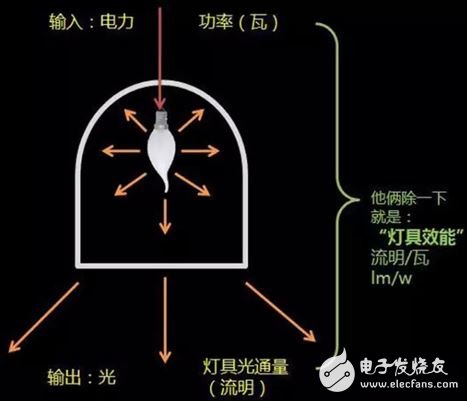
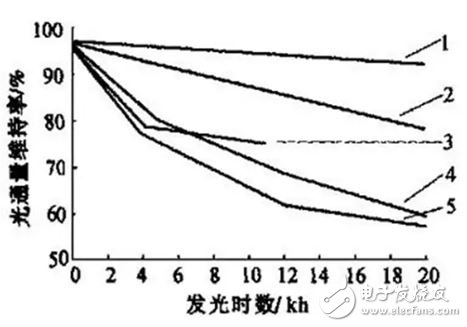
12. Luminous flux maintenance
The ratio of the luminous flux of a light source to its initial luminous flux after a given ignition time.
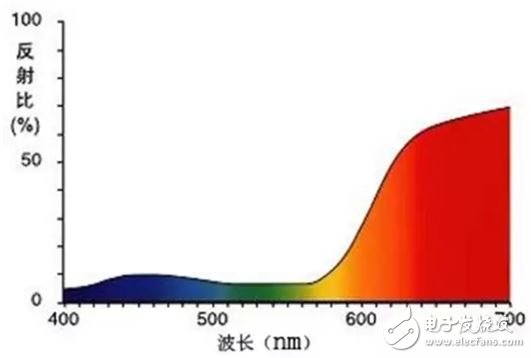
13. Reflectance ratio reflectance
The ratio of the reflected radiant flux or luminous flux to the incident radiant flux or luminous flux given the spectral composition, polarization state, and geometric distribution of the incident radiation.
14. Lighting power density lighTIng power density (LPD)
Installation power for general lighting per unit area (including auxiliary power devices such as light sources, ballasts or transformers) in watts per square meter (W/m2).
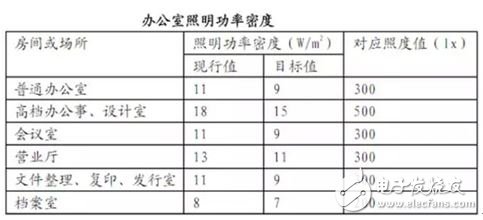
15. Room index room
A value indicating the geometry of a room or place, the value of which is twice the room or site area and the difference between the perimeter of the room or site and the difference between the height of the fixture and the height of the face.

16. Annual exposure annual lighTIng exposure
The value of the cumulative illuminance of the object is measured by the product of the illuminance received by the object and the annual cumulative hour, expressed in lux hours per year (lx·h/a).
What is an wall ap? In life, many times we will encounter a bad network situation, generally when the network is bad will affect everyone's mood, everyone likes the situation of network unobstructed, so will go to find a way to keep the network smooth, and wall ap can help you keep the network unobstructed, let's take a look.
1. wall ap
What is the wall ap is a lot of people want to know the problem, wall ap can let everyone's network has been smooth, wall ap is the most important part of the networking, wall ap and the socket at home, you can transmit signals through the wall ap, but want to really use the wall ap you need to install some network cables in each room in advance.
In other words, the wall ap can be directly called a Wireless Router, the wall ap can be used as the antenna of the router, if you put the wall ap in the room, then the signal in the room will be strengthened, but now people prefer the wireless router, so the wall ap also needs POE and AC two devices to assist.
2. AC
AC machine is the most common kind of router, it is very different from ordinary router, can not be used by simple insertion, but need to be set up several times to connect to the network, but also need to be combined with the wall ap to be better used, so the wall ap is very important. The combination of router and wall ap can enhance the network signal.
3. ap networking scheme
The ap networking scheme not only requires the wall ap, but also needs to add the control system, you can choose commercial, you can also choose home, for the network signal requirements of relatively high enterprises can choose commercial, before choosing the networking mode need to be carefully considered.
Wall Ap Wireless Ap,Wall Mount Access Point,Wall Mount Wifi Access Point,Access Point Ac In-Wall
Shenzhen MovingComm Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.mcrouters.com