The bus (Bus) is a common communication trunk line that transmits information between various functional components of a computer. It is a transmission harness composed of wires. According to the type of information transmitted by the computer, the computer bus can be divided into a data bus, an address bus, and a control bus. , Respectively used to transmit data, data address and control signal. The bus is an internal structure. It is a common channel for CPU, memory, input and output devices to transmit information. The various components of the host are connected through the bus, and the external devices are connected to the bus through the corresponding interface circuit, thus forming the computer hardware system. In a computer system, the common channel for transmitting information between various components is called a bus, and a microcomputer uses a bus structure to connect various functional components.
When the bus is idle (other devices are connected to the bus in a high-impedance state) and a device wants to communicate with the target device, the device that initiates the communication drives the bus and sends out addresses and data. If other devices connected to the bus in a high-impedance state receive (or can receive) the address information that matches their own, they will receive the data on the bus. The sending device completes the communication and gives up the bus (the output becomes a high impedance state).
3. Classification of the busA. According to functions and specifications.
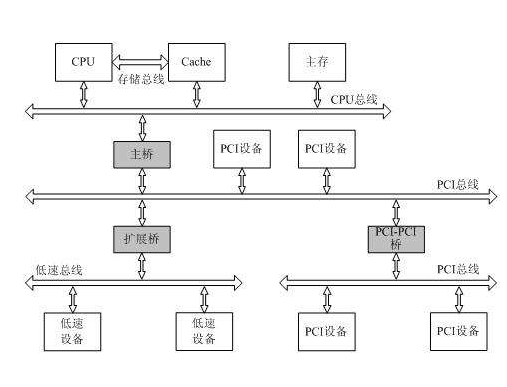
Figure 1 The position and relationship of the three types of buses in the microcomputer system
(1) Chip Bus (C-Bus), also known as component-level bus, is an information transmission path that connects various chips together to form a specific functional module (such as a CPU module). Its width can be 8, 16, 32 or 64 bits. There are several popular internal bus technologies: I2C bus, SCI bus, etc.
(2) Internal Bus (I-Bus), also known as system bus or board-level bus, is the information transmission path between the plug-ins (modules) in the microcomputer system. For example, the transmission path between the CPU module and the memory module or I/O interface module. Commonly used are PC bus, AT bus (ISA bus), PCI bus and so on.
(3) External Bus (External Bus, E-Bus)
Also known as the communication bus, it is a channel for information transmission between microcomputer systems or between microcomputer systems and other systems (instruments, meters, control devices, etc.), such as EIA RS-232C, IEEE-488, etc.
Among them, the system bus, that is, the bus in the usual sense, generally contains three busses with different functions, namely the data bus DB, the address bus AB, and the control bus CB. In some systems, the data bus and the address bus are multiplexed, that is, the signals that appear on the bus at certain moments represent data and at other moments represent addresses; while some systems are separate. The address bus and data bus of the 51 series single-chip microcomputer are multiplexed, while the bus in the general PC is separate. "Data bus DB" is used to transmit data information. The data bus is a two-way three-state bus, that is, it can transmit the data of the CPU to other components such as the memory or I/O interface, and can also transmit the data of other components to the CPU. The number of bits of the data bus is an important indicator of the microcomputer, and it is usually consistent with the word length of the micro-processing. For example, the word length of the Intel 8086 microprocessor is 16 bits, and its data bus width is also 16 bits. It should be pointed out that the meaning of data is broad. It can be real data, instruction code or status information, and sometimes even control information. Therefore, in actual work, what is transmitted on the data bus is not necessarily It's just data in the true sense. "Address bus AB" is specially used to transmit addresses. Since the address can only be transmitted from the CPU to the external memory or I/O port, the address bus is always one-way three-state, which is different from the data bus. The number of bits of the address bus determines the size of the memory space that can be directly addressed by the CPU. For example, if the address bus of an 8-bit microcomputer is 16 bits, the maximum addressable space is 2^16=64KB, and the 16-bit microcomputer (x-bit processing The device refers to the number of bits that the microprocessor can handle in one clock cycle, that is, the word length. The address bus is 20 bits, and its addressable space is 2^20=1MB. Generally speaking, if the address bus has n bits, the addressable space is 2^n bytes. The "control bus CB" is used to transmit control signals and timing signals. Some of the control signals are sent by the microprocessor to the memory and I/O interface circuits, such as read/write signals, chip select signals, interrupt response signals, etc.; there are also other components that are fed back to the CPU, such as interrupt request signals, reset Signals, bus request signals, equipment ready signals, etc. Therefore, the transmission direction of the control bus is determined by the specific control signal, which is generally bidirectional, and the number of bits of the control bus should be determined according to the actual control needs of the system. In fact, the specific situation of controlling the bus mainly depends on the CPU.
B. Divided by the way of data transmission
Can be divided into serial bus and parallel bus. In the serial bus, the binary data is sent to the destination device through a data line bit by bit; the data lines of the parallel bus usually exceed two. Common serial buses include SPI, I2C, USB and RS232. Common parallel buses include VME bus and PCI bus. The transmission speed of serial bus is faster than parallel, and the clock of parallel bus is generally 33MHz or 66MHz.
C. According to whether the clock signal is independent
Can be divided into synchronous bus and asynchronous bus. The clock signal of the synchronous bus is independent of the data, while the clock signal of the asynchronous bus is extracted from the data. I2C bus, SPI bus, PCI bus, and CPCI bus are synchronous serial buses. SCI bus, IEEE 488 and ANSI X3.131-1986 SCSI bus, VME bus, and RS232 use asynchronous serial buses.
4. The main technical indicators of the bus(1) The bandwidth of the bus (bus data transfer rate)
The bandwidth of the bus refers to the amount of data transmitted on the bus per unit time, that is, the maximum steady-state data transmission rate of MB transmitted per second. Two factors closely related to the bus are the bit width of the bus and the operating frequency of the bus. The relationship between them: the bandwidth of the bus = the operating frequency of the bus * the bit width of the bus/8 or the bandwidth of the bus = (the bit width of the bus /8)/bus cycle
(2) The bit width of the bus
The bit width of the bus refers to the number of bits of binary data that the bus can transmit at the same time, or the number of bits of the data bus, that is, the concept of bus widths such as 32 bits and 64 bits. The wider the bit width of the bus, the greater the data transfer rate per second, and the wider the bandwidth of the bus.
(3) Operating frequency of the bus
The working clock frequency of the bus is in MHZ. The higher the working frequency, the faster the bus working speed and the wider the bus bandwidth.
5. The advantages and disadvantages of the busThe main advantages of using the bus structure:
1. Simplify the hardware design. It is convenient to adopt the modular structure design method. The bus-oriented microcomputer design only needs to make cpu plug-in, memory plug-in and I/O plug-in according to these regulations, and connect them to the bus to work without considering the detailed operation of the bus.
2. The system structure is simplified. The structure of the whole system is clear. There are few connections, and the backplane connections can be printed.
3. The system has good scalability. The first is scale expansion, which only requires more plug-ins of the same type. The second is function expansion. The function expansion only needs to design new plug-ins in accordance with the bus standard, and there is often no strict restriction on the position where the plug-ins are inserted into the machine.
4. Good system update performance. Because the cpu, memory, I/O interface, etc. are all connected to the bus according to the bus protocol, as long as the bus is properly designed, new plug-ins can be designed at any time along with the progress of the processor chip and other related chips. The system is updated on the bottom board, other plug-ins and backplane connections generally do not need to be changed.
5. It is convenient for fault diagnosis and maintenance. The mainboard test card can easily find the faulty part and the bus type.
Disadvantages of using the bus structure:
1. It is time-sharing using bus transmission. When multiple masters apply for the use of the bus at the same time, arbitration of the bus must be carried out.
2. The bandwidth of the bus is limited. If the hardware devices connected to the bus do not have a resource control mechanism, it is easy to cause information delay (this is fatal in some places with strong immediacy).
3. The device connected to the bus must have a screening mechanism for information, and it is necessary to judge whether the information is passed to itself.
Embedded bus technology classification
1. Internal bus, system bus and external bus
1. Internal bus
Internal Bus: Connect all structural units of the processor internally. Its width can be 8, 16, 32, or 64 bits. Several popular internal bus technologies at present:
I2C bus
The I2C (Inter-IC) bus was introduced by Philips more than 10 years ago. It is a new type of bus standard widely adopted in the field of microelectronic communication control in recent years. It is a special form of synchronous communication, which has the advantages of fewer interface lines, simplified control mode, small device package form, and higher communication speed. In master-slave communication, there can be multiple I2C bus devices connected to the I2C bus at the same time, and the communication object can be identified through the address. SPI bus
Serial peripheral interface SPI (serial peripheral interface) bus technology is a synchronous serial interface introduced by Motorola. Most MCUs (microcontrollers) produced by Motorola are equipped with SPI hardware interfaces, such as 68 series MCUs. The SPI bus is a three-wire synchronous bus. Because of its strong hardware functions, the SPI-related software is quite simple, allowing the CPU to have more time to process other transactions. SCI bus
The serial communication interface SCI (serial communicaTIon interface) is also introduced by Motorola. It is a universal asynchronous communication interface UART, which is basically the same as the asynchronous communication function of MCS-51.
2. System bus
System bus is also called internal bus or board-level bus. Because this bus is used to connect the functional components of a microcomputer to form a complete microcomputer system, it is called a system bus. Commonly used are PC bus, AT bus (ISA bus), PCI bus and so on.
The information transmitted on the system bus includes data information, address information, and control information. Therefore, the system bus contains three busses with different functions, namely data bus DB (Data Bus), address bus AB (Address Bus) and control bus CB (Control Bus). Bus)
Several popular system bus technologies at present: ISA bus
ISA (industrial standard architecture) bus standard is a system bus standard established by IBM in 1984 for the introduction of PC/AT machines, so it is also called AT bus. It is an extension of the XT bus to meet the requirements of the 8/16-bit data bus. It was widely used in the 80286 to 80486 era, so that there is still an ISA bus slot in the Pentium machine. The ISA bus has 98 pins.
Smart Board For Conference,Whiteboard Smart Board,Interactive Whiteboard Smart Board,Smart Board Interactive Whiteboard
APIO ELECTRONIC CO.,LTD , https://www.apiodisplays.com