The ICMP protocol plays a crucial role in network communication. When studying network protocols, this part is often one of the key areas we focus on. Understanding how ICMP works and what it does is essential for grasping the fundamentals of network troubleshooting and management. Let’s dive deeper into its functionality and explore the core concepts behind it.
**Introduction to ICMP**
For anyone familiar with the internet, ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) is a well-known component of network communication. It operates at the network layer of the OSI model, similar to the IP protocol. Its primary function is to send error messages and operational information between devices on a network. The main roles of ICMP include:
- **Host detection**: Identifying whether a host is active or reachable.
- **Route maintenance**: Helping in updating and maintaining routing tables.
- **Routing**: Assisting in directing data packets along the best path.
- **Flow control**: Managing the rate of data transmission to prevent congestion.
There are multiple methods to detect a host, such as using BANNER services, applications, or tools like NMAP. However, one of the most common techniques involves the use of the ICMP protocol. This method helps in understanding the behavior of the protocol and its importance in network operations.
**Protocol Analysis – Detailed ICMP Protocol Decoding**
ICMP, short for Internet Control Message Protocol, is a critical part of the TCP/IP suite. It operates at the network layer and is used to report errors and provide feedback during data transmission. Since the IP protocol is connectionless, it doesn’t handle errors on its own. That’s where ICMP comes in—it fills that gap by providing error messages back to the source.
When data is transmitted across a network, unexpected issues can occur, leading to packet loss or delivery failures. ICMP helps identify these problems and allows for fault isolation and recovery. It sends messages to inform the sender about issues such as unreachable destinations, packet timeouts, or routing changes.
ICMP supports various message types, which can be categorized into five main groups:
- **Echo Request and Echo Reply** (Type 8, Code 0; Type 0, Code 0)
- **Destination Unreachable** (Type 3, Codes 0–15)
- **Redirect Messages** (Type 5, Codes 0–4)
- **Time Exceeded** (Type 11, Codes 0–1)
- **Information Messages** (Types 12–18)
These messages help network devices understand and respond to different conditions, making ICMP an essential tool for network diagnostics.
**Detailed Decoding**
Using a network analysis tool like Wireshark, we can capture and analyze ICMP packets. For example, an ICMP echo request and reply can be observed in action, as shown in Figure 1.
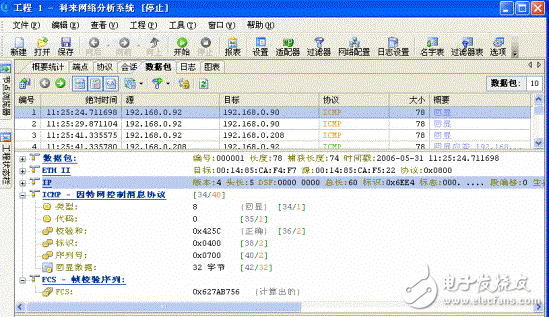
**ICMP Protocol Content**
The full name of ICMP is Internet Control Message Protocol. From a technical perspective, it serves as an “error detection and reporting mechanism,†helping to monitor and ensure the reliability of network connections. Its key functions include:
- Detecting whether a remote host is active.
- Establishing and maintaining routing information.
- Redirecting data paths when necessary.
- Controlling data flow to prevent overload.
ICMP uses different message types (defined by the "Type" field) and codes (the "Code" field) to convey specific conditions. These are vital for machines to interpret network status accurately.
**The Importance of the ICMP Protocol**
ICMP is not only useful for diagnostics but also plays a significant role in network security. Due to its nature, it can be exploited for malicious purposes. For instance, in August 1999, a firewall was attacked over 334,050 times through ICMP, accounting for more than 90% of all attacks. This highlights the potential risks associated with the protocol.
One well-known attack is the "Ping of Death," which exploits the maximum size limit of ICMP packets. If a packet exceeds 64 KB, it can cause memory allocation errors, crashing the system's TCP/IP stack.
Additionally, flooding a target with large volumes of ICMP packets can lead to an "ICMP storm," overwhelming the system’s CPU and causing it to become unresponsive.
**ICMP Protocol Checksum Algorithm**
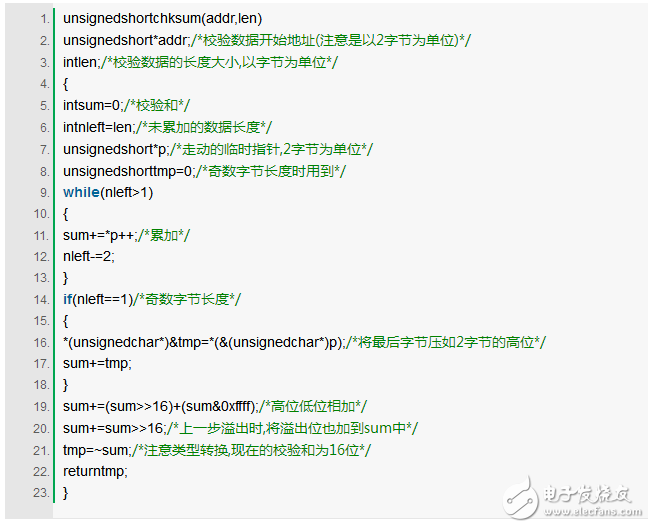
We often use the ICMP protocol without even realizing it. For example, when we run the "Ping" command to check if a network is functioning, we’re interacting with ICMP. Similarly, the "Tracert" command (or "traceroute" on Unix-based systems) relies on ICMP to trace the path data takes across the network.
In summary, the ICMP protocol is a fundamental part of network communication, serving both diagnostic and security-related functions. Understanding its operation is essential for anyone working with networks, whether for troubleshooting, monitoring, or securing them.
Application: Automobile Wire Harness
Place of Origin:Dongguan, China (Mainland)
Gauge: AWG 28 to AWG 16
Length: Customized
A perfect replacement of the broken or old windshield washer nozzle
Connector: Molex, JST, TYCO, AMP, JAM, KET,Amphenol, Wago,Weidmuller, Phoenix,
Wires & Cables: UL, VDE standards
Inspection: 100% inspection before delivery
Certification UL, IATF16949, CE,
Features:
Superior plastic material. High quality and new brand
Working well with the washer wiper
Easy to install. Reliable craft
Durable. Not easy to be blocked by water
Car Wiper Blades,Obd Jumper Harness,Electrical Cable Gland,Auto Wiper Blade
Dongguan YAC Electric Co,. LTD. , https://www.yacentercn.com