The term "wearable" indicates that the device is either a device that is worn directly on the human body, or a piece of clothing, and has a suitable design to support its use as a wearable accessory. Broadly speaking, this requires the device to be extremely small in size and weight, functionally autonomous, self-contained, easy to use, and comfortable to wear.
Smart wearable healthcare devices and typical architectureA wearable healthcare device can be defined as a non-invasive system that can self-monitor or support specific medical functions. (The national standard for wearables is under development)
There are many types of smart wearable healthcare devices, such as wristbands, watches, glasses, and other wearable types. Functions performed include pedometer, heart rate monitoring, motion recording, bioelectrical potential measurement, bioimpedance measurement, oximetry, and the like.

Smart wearable healthcare devices are an extension of traditional medical devices. The typical hospital medical equipment is large in size, complex in structure, and high in power consumption, and is intended for high-precision clinical applications. With the development of sensors and semiconductor technology, device size and power consumption are much smaller than before, making wearable devices a reality. Many of the technologies used in hospital clinics have moved from hospitals to homes or to various wearable devices. Smart wearable healthcare devices are often non-invasive vital sign monitoring devices that are easy to use and wear. In order to enhance the user experience, the lighter the weight, the lower the power consumption, the better. It also provides connectivity to other consumer electronics devices.
Design considerations and major challenges
Size ( very important, most wearables are light and smaller )
Smaller package
Advanced packaging technology to increase integration
I hope that the fewer external components, the better.
Ultra low power consumption
Power consumption is critical to the user experience, the lower the better
Limited battery size due to system size
Low quiescent current chip facilitates low power consumption and extended standby time
Wearable devices typically require a low-power MCU
Wearable devices require low-power connectivity
Ergonomic design
Easy to use
Prevent misoperation design
Highly reliable, highly sensitive sensor design
High reliability
Adapt to various environments
Good mechanical design to prevent equipment damage
Sometimes the device needs to be waterproof
Sensor Technology
Multi-sensor fusion
Choose sensor materials with good biocompatibility
High sensitivity at low power consumption
Connection technology
Need low-power Bluetooth, WIFI connection to access other smart devices
Data synchronization and application auto-upgrade
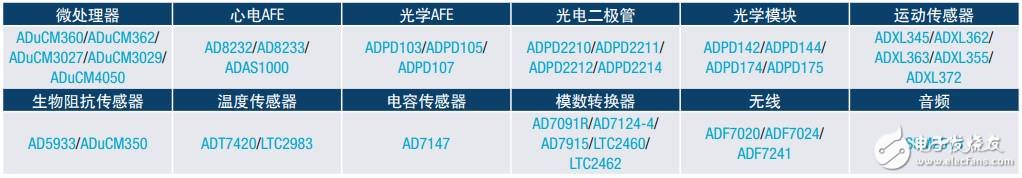
ADI's total solution
ADI offers a wide range of highly integrated AFEs, motion sensors, low-power MCUs and power management solutions to optimize the quality and reliability of wearable devices. In addition, Analog Devices offers evaluation boards, simulation tools, and application expertise to support customers' design and development efforts.
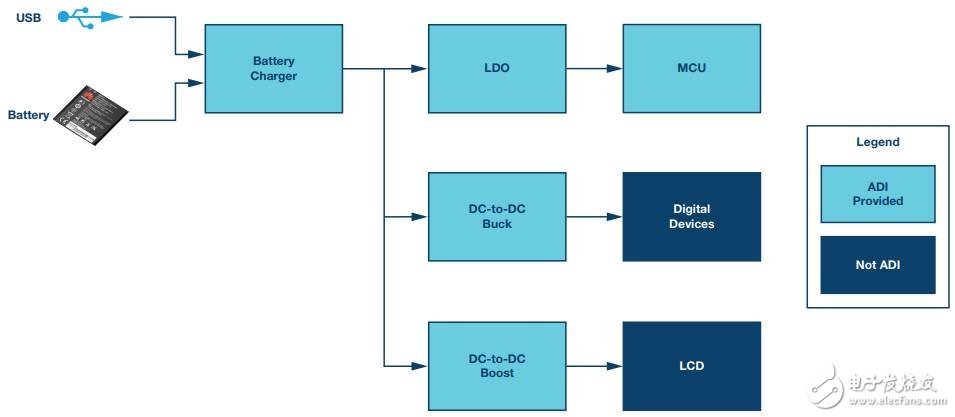
Main signal chain
Note: The above signal chain represents a smart wearable healthcare device system. The technical requirements of the modules may vary in the specific design, but the products listed in the table below represent the ADI solutions that meet some of the requirements.
 |
ALL Kinds of 4G Cat-4 Vehicle GPS Tracker, there must be one which should meet your expectation.
ES810-C4 the one supports WIFI and Hotspot
ES811-C4 the waterproof version of ES810-C4
CAT-4 vehicle GPS Trackers,CAT-4 car GPS Trackers,Waterproof CAT-4 vehicle GPS Tracker,IP65 CAT-4 vehicle GPS Tracker
eSky wireless Inc , https://www.eskygpsiot.com