Magnetic resonance imaging [MagneTIc Resonance, MR] is a method of medical examination, and a revolution in medical imaging. The biological tissue can be penetrated by short-wave components such as X-rays in the electromagnetic spectrum, but can block the medium wave component. Such as ultraviolet light, infrared light and long waves. Human tissue allows long-wave components such as radio waves generated by magnetic resonance to pass through, which is one of the basic conditions for the application of magnetic resonance in clinical practice.
What is nuclear magnetic resonance?The nuclear spin motion is the basis of magnetic resonance imaging, and the hydrogen atom is the most abundant substance in the human body; under normal circumstances, the hydrogen nuclei in the human body are in an irregular precession state, when the human body enters a powerful and uniform magnet space, Under the action of static magnetic field, the original disordered hydrogen nuclei are arranged in the direction of the external magnetic field and continue to move. When the external magnetic field is stopped immediately, the hydrogen atoms in the human body will return to the original state at the same time in the same tissue; this is called relaxation. [RELAXATION] The human tissue relaxation time under pathological conditions is different. These signals are collected by computer system and converted into images by digital reconstruction technology to provide scientific diagnosis results for clinical and research.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), for high resolution of soft tissue synovium, blood vessels, nerves, muscles, tendons, ligaments, and hyaline cartilage, for inflammation of the synovium, blood vessels and muscles, fascia, synovial cysts, and Clinical examination of hyaline cartilage degeneration, exfoliation and destruction of ischemic necrosis, cervical and nucleus lesions, knee meniscus and cruciate ligament injury, rheumatoid neurological complications and osteomyelitis. Can determine the macroscopic conditions of synovial inflammation, such as the extent and extent of fibrin exudation when the synovial volume changes, cell infiltration, vascular proliferation and granuloma (vasospasm) formation, synovial villi and synovial hypertrophy Early and its disease activity. Can also distinguish myositis, fascia tension, fat penetration and hypertrophy and inflammation and growth. Can clearly show cervical dislocation, spinal cord compression and spinal cord distortion.
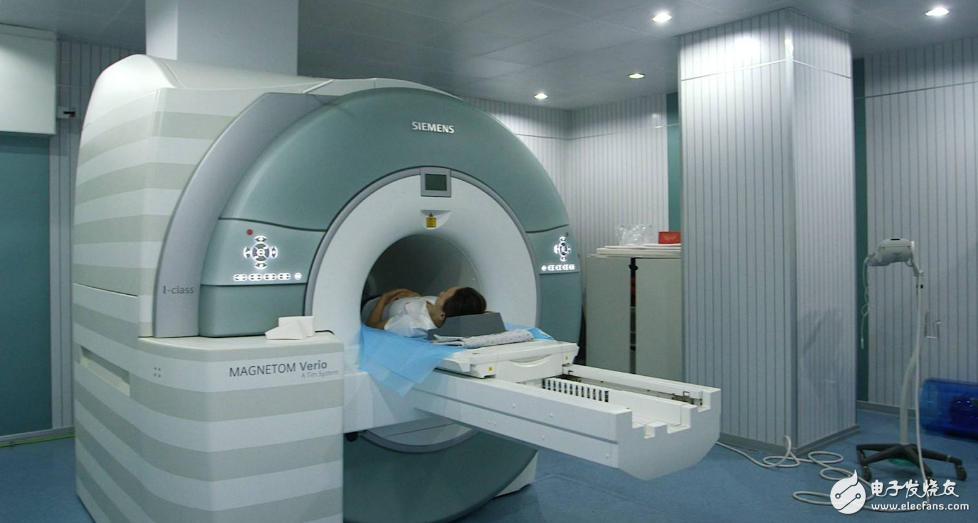
Check indication
Central Nervous System
1. Intracerebral vascular lesions 2. Brain tumors 3. Various spinal cord lesions 4. Intracranial infections 5. Degenerative changes in the brain 6. Cranial congenital malformations 7. Craniocerebral trauma
ENT
1. Intraocular inflammation, intraorbital tumor, intraorbital vascular disease 2. Paranasal sinus inflammation, tumor 3. Tongue tumor 4. Parotid lesion 5. Ear various tumors
chest
1. Heart and macrovascular malformations and tumors 2. Mediastinal tumors and mediastinal fistulas 3. Congenital malformations of the lungs, pulmonary vascular lesions and tumors 4. Breast inflammation, hyperplasia and tumors.
abdomen
1. Hepatic cyst, hemangioma, liver cancer 2. Biliary calculi, tumor 3. Spleen, kidney, pancreas contusion, inflammation and tumor 4. Prostatic hyperplasia, tumor 5. Ovarian, uterus congenital malformation and tumor
Musculoskeletal system
1. Shoulder joint, knee joint injury 2. Avascular necrosis of the femoral head 3. Skeletal inflammation and tumor
Precautions
Magnetic resonance imaging has the advantages of safety, non-radiation, precision, etc., to ensure that the following points can be used for magnetic resonance examination:
1. If there are magnets in the body, such as a pacemaker, a prosthetic valve, and a metal foreign body residue beside the important organs, this test cannot be performed, but the implant in the body is confirmed by the surgeon as a non-magnetic object. Magnetic resonance examination.
2. Explain to the technician the following conditions: whether there is a history of surgery; whether any metal or magnetic substance is implanted in the body including metal birth control rings; whether there are dentures, electronic ears, prosthetic eyes, etc.; whether there is drug allergy; whether there is metal Foreign matter splashed into the body.
3. Do not wear underwear with metal materials. Patients with head and neck should wash their hair one day before the test. Do not wipe any hair care products.
4. Before the inspection, remove all the clothes outside the underwear and replace the special clothes for the magnetic resonance room. Remove the metal items such as necklaces, earrings, watches and rings. Remove cosmetics and dentures, prosthetic eyes, glasses and other items on your face.
5. Before the examination, provide the doctor with all medical history, examination data and all X-ray films, CT films, and previous magnetic resonance films.
6. Abdominal (liver, spleen, kidney, pancreas, biliary tract, ureter, etc.) inspectors were fasted for 4 hours before the examination, and 654-2 were injected before the examination.
7. Magnetic resonance urography (MRU) was performed before the examination of oral furosemide 20mg.
8. Do a mental preparation for magnetic resonance examination, do not be impatient, afraid, follow the guidance of the doctor, patiently cooperate.
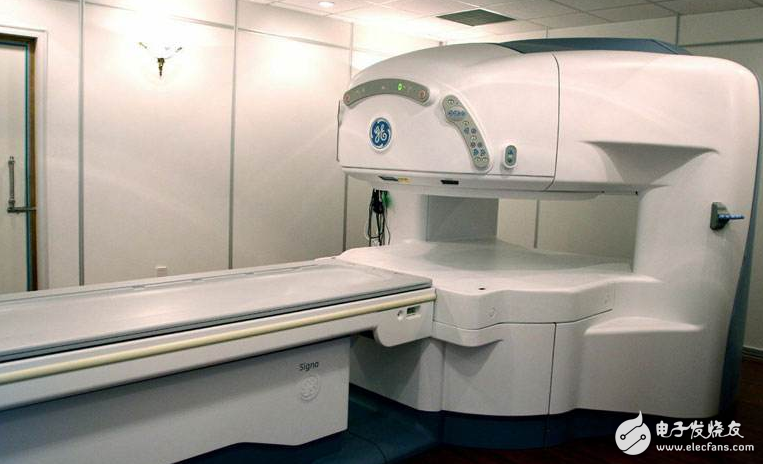
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is an imaging technique that reconstructs an image by collecting signals generated by magnetic resonance phenomena. Therefore, it is also called spin layer imaging and nuclear magnetic resonance CT. MRI can make the development of lesions that CT does not show is another major development in the field of medical imaging. It is a new imaging diagnostic technology that was only used in the early 1980s. Compared with CT, it has no radiation damage, no bony artifacts, multi-faceted, multi-parameter imaging, high soft tissue resolution, and unique advantages such as vascular structure without the use of contrast agents.
It is suitable for almost all diseases of the whole system, such as tumors, inflammation, trauma, degenerative diseases and various congenital diseases. The display of brain, spinal and myelopathy is superior to CT. It can use angiographic contrast agents, which show the structure of blood vessels, so it has its own unique features for the mutual identification of blood vessels, tumors, lymph nodes and vascular structures. It also has a soft tissue resolution that is several times higher than CT, sensitively detecting changes in water content in tissue components, and thus often finding lesions more efficiently and earlier than CT. MRI can clearly and comprehensively display the heart cavity, myocardium, pericardium and other small structures in the heart. It is a reliable method for diagnosing various heart diseases and heart function tests.
Computed tomography (CT) can accurately detect small differences in density between different tissues on a transverse anatomical plane. It is an ideal method for observing bone and soft tissue lesions. In the diagnosis of arthritis, it is mainly used to check the spine, especially the ankle joint. CT is superior to traditional X-ray examination in that it has high resolution and can also perform axial imaging.
Due to the high density resolution of CT, soft tissues, bones and joints can be seen clearly. In addition, CT can do axial scanning, and some joints that are difficult to distinguish on conventional X-ray images can be "original" on the image. For example, because the joint surface of the ankle joint is born to be inclined and curved, and there are overlaps of other tissues, although most cases of the ankle joint X-ray film may have met the requirements, sometimes X-ray examination found that the arthritis comparison If you have difficulty, you can have a CT scan on the patient with the problem.
12.8V150Ah Lithium Iron Phosphate Battery
FEATURES & BENEFITS
Saintish lithium iron batteries use top quality cells, which are auto grade A LiFePO4 cells with higher energy density, more stable performance . UL approved for the cells inside the battery.
The lithium-ion batteries are perfect for solar system, caravan, RVs, campers, Yacht, off-grid applications and lead aicd replacement.
The Lithium Iron Phosphate Battery provides 3000+ cycles (@100%DoD) and 10 years lifespan. which is 10 times than lead-acid battery. 1/3 of the weight of lead acid, Saintish LiFePO4 Battery weighs only 20.8kgs each pc, but delivers twice power.
Saintish lithium iron phosphate battery has built-in BMS to protect it from overcharge, over-discharge, over current, and short circuit with excellent self-discharge rate. Operating Temperature: Charge: 0°C~45°C; Discharge: -20°C~60°C.
SPECIFICATIONS
| Rated Capacity | 150Ah | Charge Temperature | 0-45℃ |
| Nominal Voltage | 12.8V | Connection Method | Parallel & Series |
| Energy | 1920Wh | Dimensions | 483*170*240mm |
| Cycle Life | >3000@100% DOD | Weight | 20.8KG |
| Maximum Charging Current | 50A | Terminal Torque | 12-15N.m |
| Maximum Continuous Discharging Current | 100A | Enclosure Protection | IP65 |
| Discharging Voltage Range | 8.4-15.2V | Max. Batteries in Series | 4 |
| Charging Voltage Range | 14.4-15.2V | Certifications | CE, UN38.3, MSDS |
| Discharge Temperature | -20-60℃ | Warranty | 5 Years |
LiFePO4 Battery 150Ah, 150Ah Battery, Lithium Phosphate Battery, Lithium Iron Battery
Hangzhou Saintish Technology Co.,Ltd. , https://www.saintishtech.com