With the advent of artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things era, data applications have become more frequent, and how should data security be protected? What are the software encryption algorithms, and in which aspects are these algorithms applied? Read it slowly and you will find the "small password" around us.
Symmetric encryption algorithmThe symmetric encryption algorithm is an early encryption algorithm and the technology is mature. In the symmetric encryption algorithm, the data sender sends the plaintext (raw data) together with the encryption key through a special encryption algorithm, and then sends it into a complex encrypted ciphertext. In the symmetric encryption algorithm, there is only one key used, and both the sending and receiving parties use this key to encrypt and decrypt the data, which requires the decrypting party to know the encryption key in advance. The characteristics of the symmetric encryption algorithm are that the algorithm is open, the calculation amount is small, the encryption speed is fast, and the encryption efficiency is high. The downside is that both sides of the transaction use the same key and security is not guaranteed. Symmetric encryption algorithms are more difficult to use on distributed network systems, mainly because of the difficulty in key management and high cost of use.

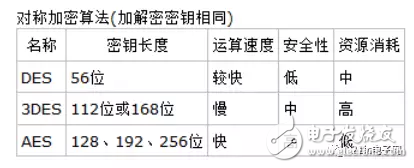
The DES encryption algorithm is a block cipher that encrypts data in packets of 64 bits. Its key length is 56 bits, and the same algorithm is used for encryption and decryption. The DES encryption algorithm keeps the key secret and exposes the algorithm, including encryption and decryption algorithms. Thus, only those who have mastered the same key as the sender can interpret the ciphertext data encrypted by the DES encryption algorithm. Therefore, deciphering the DES encryption algorithm is actually the encoding of the search key. For a 56-bit key, if the search is performed by an exhaustive method, the number of operations is 256.
With the continuous development of computer system capabilities, the security of DES is much weaker than it was when it first appeared. However, from the reality of non-critical nature, it can still be considered sufficient. However, DES is now only used for the authentication of legacy systems, and more to choose new encryption standards.
3DES encryption algorithm3DES is a generic term for triple-data encryption algorithm block ciphers. It is equivalent to applying three DES encryption algorithms to each data block. Due to the enhancement of computer computing power, the key length of the original DES password becomes easy to be brute force cracked; 3DES is designed to provide a relatively simple method to avoid similar attacks by increasing the key length of DES. Not a new block cipher algorithm.
3DES is an encryption algorithm for DES to AES transition. The encryption algorithm is implemented as follows: Ek() and Dk() represent the encryption and decryption process of DES algorithm, K represents the key used by DES algorithm, M stands for plaintext, C stands for Cipher text, like this:
The 3DES encryption process is: C=Ek3(Dk2(Ek1(M)))
The 3DES decryption process is: M=Dk1(EK2(Dk3(C)))
The AES encryption algorithm is an advanced encryption standard in cryptography. The encryption algorithm uses a symmetric block cipher system. The minimum key length is 128, 192, and 256, and the packet length is 128 bits. The algorithm should be easy to implement in various hardware and software. This encryption algorithm is a block encryption standard adopted by the US federal government. This standard is used to replace the original DES and has been analyzed by many parties and widely used around the world.
The AES encryption algorithm is designed to support 128/192/256 bits (/32=nb) block size (ie packet length); 128/192/256 bits (/32=nk) password length is supported, in decimal Corresponding to 34&TImes; 1038, 62 & TImes; 1057, 1.1 & TImes; 1077 keys.
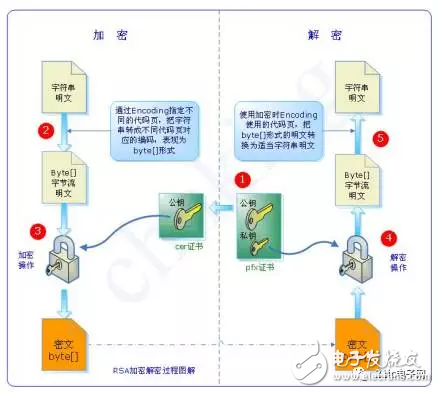
The asymmetric encryption algorithm uses two completely different but perfectly matched pairs of keys—public and private. When encrypting a file using an asymmetric encryption algorithm, the encryption and decryption process of the plaintext can be completed only by using a matching pair of public and private keys. Using the asymmetric encryption algorithm, before the sender and the receiver communicate, the receiver must send the public key that has been randomly generated to the sender, and retain the private key. Since the asymmetric algorithm has two keys, it is especially suitable for data encryption in distributed systems. The widely used asymmetric encryption algorithms are the RSA algorithm and the DSA proposed by the US National Bureau of Standards. Encryption technology based on asymmetric encryption algorithms is widely used.
RSA encryption algorithmRSA encryption algorithm is currently the most influential public key encryption algorithm, and is generally considered to be one of the best public key solutions. RSA is the first algorithm that can be used for both encryption and digital signatures. It is resistant to all password attacks known to date and has been recommended by ISO as a public key data encryption standard. The RSA encryption algorithm is based on a very simple number theory fact: it is very easy to multiply two large prime numbers, but at that time, but it is extremely difficult to factorize the product at that time, so the product can be exposed as an encryption. Key.
DSA is based on the integer finite-domain discrete logarithm problem, and its security is similar to that of RSA. An important feature of DSA is that two prime numbers are exposed, so that when you use someone else's p and q, you can confirm whether they are randomly generated or not, even if you don't know the private key. The RSA algorithm does not. DSA is just an algorithm. It differs from RSA in that it cannot be used for encryption and decryption, nor for key exchange. It is only used for signatures. It is much faster than RSA.
Doorbell speaker:
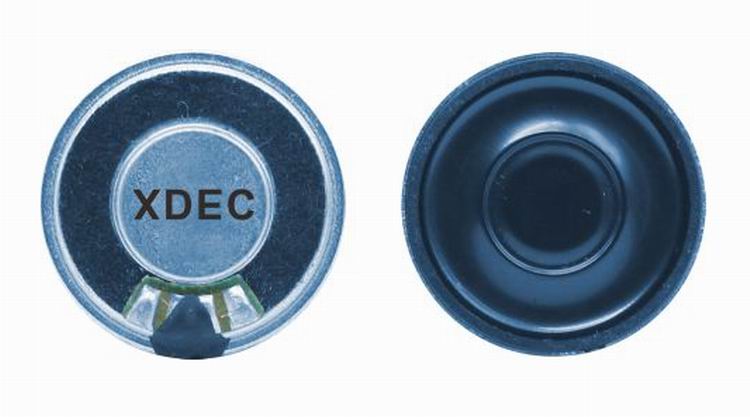
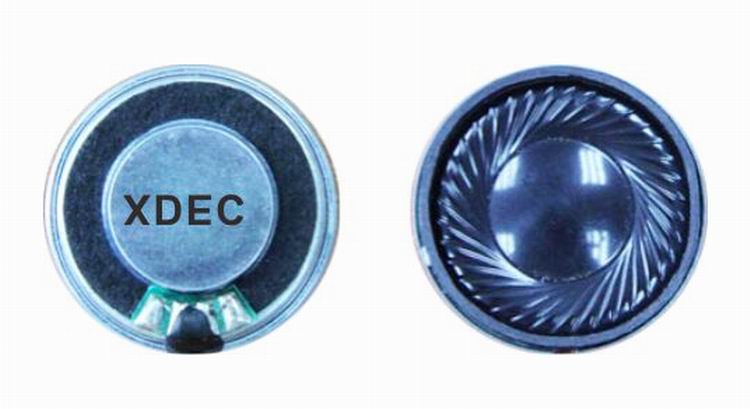
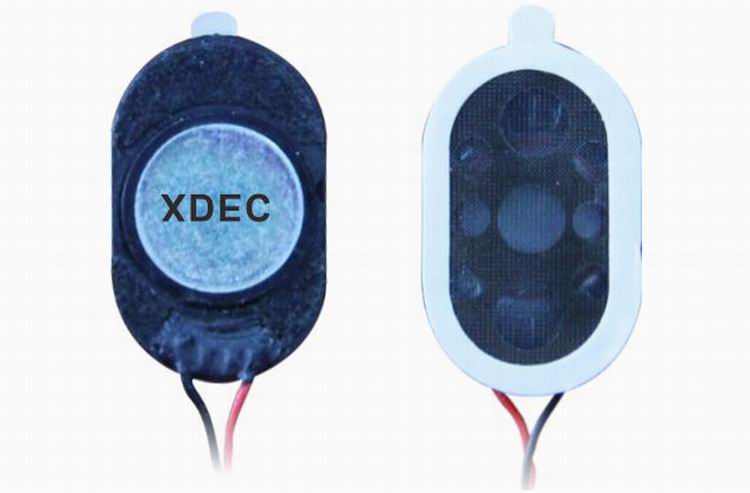
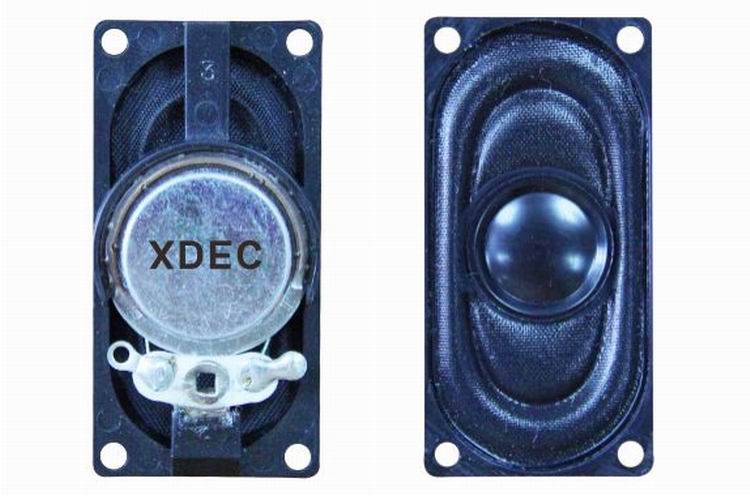
Doorbell speaker is a kind of micro speaker unit which uses a diaphragm made of Mylar material. Doorbell speakers are of ultrathin design and lightweight and clear voice. It is widely used in building security industry (e.g. intercom, video door phone, intelligent door control..)
There are two types of Mylar speakers from the shapes:
1) Round shapes, we have products from 10mm to 57mm in diameter.
2) Oblong shape, we have products in sizes of 1510/1712/1813-..




FAQ
Q1. What is the MOQ?
XDEC: 2000pcs for one model.
Q2. What is the delivery lead time?
XDEC: 15 days for normal orders, 10 days for urgent orders.
Q3. What are the payment methods?
XDEC: T/T, PayPal, Western Union, Money Gram.
Q4. Can you offer samples for testing?
XDEC: Yes, we offer free samples.
Q5. How soon can you send samples?
XDEC: We can send samples in 3-5 days.
Doorbell Speaker,Doorphone Speaker,Video Doorphone Speaker,Doorbell Wireless Speakers
Shenzhen Xuanda Electronics Co., Ltd. , https://www.xdecspeaker.com