RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) is an automatic wireless identification and data acquisition technology that has been widely used in many fields. This paper introduces the performance characteristics of mainstream RFID technology, and analyzes the application trends and technology development trends of the technology in the future.
RFID is an automatic wireless identification and data acquisition technology that has been used for many years and has more and more applications. Today, smart chips with readable and writable memory that protects against unauthorized access are already visible in many containers, pallets, product packaging, smart ID cards, books or DVDs. Due to possible future applications, RFID is about to enter a period of tremendous growth. The global market for such technologies, chips, card readers, software and services will grow from $1 billion in 2002 to $2.6 billion in 2007.
Applications will continue to focus on the supply logistics sector, where RFID transceivers are used to record and track a wide range of mobile goods/products in RFID transceivers (credit-sized plastic/paper labels, included) The necessary storage on the chip, RF section and antenna) will continue to be a major application. Another possible application is to attach transceiver tags to textiles, pharmaceutical packaging or even individual kits. However, in the future, RFID will also be used in areas such as local public transportation, car remote control keys, transmission of tire pressure, and in mobile phones. Rapid identification is important for the company's logistics program, the transportation of large warehouses, clinics or goods, and in business. For example, the car table and chair must be color ordered into the assembly line at the correct time; the smart tag will automatically detect that the correct drug container is moved from the storage to the production site; the blood sample will correspond exactly to the patient who collected the blood sample; The supply of fresh goods required by supermarkets requires a very complex transmission network. This network does not allow errors; there will be no fake tickets for the 2006 World Cup Cup tickets, thanks to the RFID chip.
Another focus of the future is in the automotive industry, such as controlling mirrors, all electric motors and automotive door lighting. Looking further afield, e-ticketing, 'e-passport', and even proprietary communications services have revealed an opportunity for RFID-IC applications. Bundesbank of Germany expects RFID to be used in banknotes. This type of banknote is different from today's banknotes and cannot be simply forged by color printers or copiers. In fact, it is necessary for chip manufacturers to produce RFID that is as thin as paper and as large as sand. -IC.
The best RFID technology: to meet the applicationA number of facts have proven that major sales opportunities exist in the logistics process, and different technologies can be used depending on industry and performance requirements (eg, read speed, number of RFID tags that need to be read simultaneously). RFID technology can be basically divided into low frequency system, high frequency (HF) system with frequency of 13.56MHz and UHF system with frequency band around 900MHz, and working in 2.4GHz or 5.8GHz (see table) microwave frequency band. system. In addition to the frequency range, another difference is the power supply: passive RFID transceivers, which are used primarily for logistics and target tracking. They do not have a power supply themselves, but instead derive energy from the RF field of the reader/writer; The transceiver is battery powered and therefore has a long distance of tens of meters, but is bulkier and, most importantly, more expensive.
Important parameters of RFID technologyThe low-frequency RFID chip (passive) works at a frequency of around 130 kHz. The current main applications are in access control, animal ID, electronic lock frame, and machine control authorization check. The slow read speed of this technology is not a problem, because only very short information needs to be transmitted in one direction. The corresponding ISO standards are 11484/85 and 14223. The 13.56 MHz system will become more and more important in many industrial fields. Classified as a passive class, it has a high degree of miniaturization and has been continuously improved in recent years. The system used to obtain goods and product information and conforms to ISO standards 14443, 18000-3, 1 is relatively slow. In some cases, a read operation takes several seconds, and different data volumes require different specific times. . Depending on the type, ISO 15693 standard type systems can handle moving targets with a maximum speed of 0.5 m/s, and can achieve data transmission speeds of up to 26.48 kbps, enabling recognition of 30 objects per second.
However, in the future large-scale logistics applications, the traditional methods working at 13.56 MHz, even the most recent methods defined in ISO 15693, are not sufficient. Phase Jitter Modulation (PJM) technology has emerged in this application. PJM's RFID tags are suitable for high-speed access to the marked object anywhere on the conveyor belt and must be read at very high data rates, such as identifying packaged drugs, airport baggage tracking or up to 1.2 km The distance of the ruler is logged in to the document.
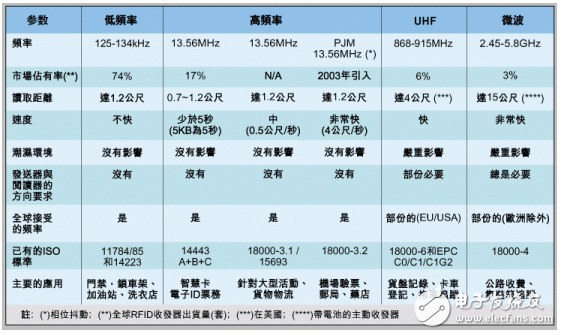
Table: Comparison of major RFID technologies.
Continuous switching between 8 RF channels increases read speed and ensures reliable identification, even at high throughput rates. Based on Magellan's PJM technology, Infineon and Australia's Magellan Technologies have teamed up to develop chips for this purpose. Compared to the current 13.56MHz RFID technology, these chips can provide up to 25 times faster read and write speeds and data rates up to 848kbps. The PJM system is optimized for logistics (ISO Standard 18000-3 Mode 2), which reliably identifies, reads and writes up to 500 electronic labels in less than a second. The readers for these new chips are capable even at target speeds of 4 meters per second.
The 10Kb of available memory space is equivalent to approximately two DIN A4 pages of simple text storage. This memory space can be further divided into several sectors, and only authorized persons can read and write access. Special encryption methods prevent unauthorized access to stored data.
UHF and microwave systems can eventually allow a reach distance of a few meters; they usually have their own batteries and are therefore suitable for identification of large cargo such as in pallets on loading ramps, or even vehicle chassis in the automotive industry. . A disadvantage of these frequency ranges is the negative effects of atmospheric humidity and the need to maintain the orientation of the transceiver relative to the read/write antenna from time to time or always.
Application-oriented technologyIt is usually always a specific application to dominate which technology to adopt. For department stores, it is of no point to label the goods just to facilitate reading at the point of sale, because in the current cost environment, this makes the product more expensive. However, the following application is very meaningful: when a library lends a book or a CD, the 13.56MHz tag attached to the book or CD can be read in a few seconds, or at the drug wholesaler's selection. The drug is reliably identified on the conveyor belt to avoid false alarms that may cause serious consequences.
Basically, however, any object reading, identification, and tracking task can benefit from well-thought-out RFID technology applications, especially when each data must be written to the chip, modified by authorized users, and prevented from being segmented. Unauthorized access to memory - possibly even at very high speeds and simultaneous processing of large numbers of objects.
Will the barcode be gradually out?This question may have been based on the facts mentioned above, but the answer is no. For reasons of cost, a 0.25-euro cheese pot sold in the supermarket will continue to use barcodes for a long time. However, it is absolutely conceivable that in the next three to five years, the current use of bar codes will be open for RFID tags, such as the identification of large items such as textiles or parcels, as well as the payment of urban public transport or unmanned vending machines. In all of these applications, RFID operating at 13.56 MHz is advantageous over bar codes in terms of reliability, avoidance of contamination, visibility, read speed and spatial directionality, not to mention the problems caused by contact, theory. Up (RFID) can read and write indefinitely.
RFID tag costs are fallingThe cost of RFID technology is related to the actual application. Depending on the size of the antenna attached to the metal substrate (currently 7.5 cm & TImes for 13.56 MHz; 4.5 cm or 4.5 cm & TImes; 4.5, 5 cm diameter for loop antennas for CD), in the case of quantities up to 1 million The cost of embedding RFID (ie, the chip, the connection to the antenna, the antenna on the substrate material) is about 50 points. This will change in the next two to three years: as fast as 2006 or 2007, it will reach 20 cents, about 50% of the cost of the chip, and the other half of the cost of the antenna and substrate material (foil and paper) , or adhesive layer). The cost is of course related to the size of the antenna and the quality of the foil or paper, for example hologramed paper will necessarily make the RFID tag more expensive.
The technology behind RFIDThe RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) system consists of two parts: a read/write unit and an electronic transceiver. The reader emits electromagnetic pulses through the antenna, and the transceiver receives the pulses and sends the stored information to the reader as a response. In fact, this is a non-contact read, write or delete process of the data in memory. Technically, a 'smart tag' contains an RFID circuit that includes an RFID chip with an RFID radio frequency portion and an ultra-thin antenna loop that is embedded in the tag along with a plastic sheet. Usually, a label is attached to this label, and some important information can be clearly printed on the label. Current smart labels are typically credit card sizes, for small goods, 4.5 & TImes; 4.5 cm size labels, and 4.7 cm diameter circular labels for CDs and DVDs. The advantage of transceiver technology over other ID technologies like bar codes or magnetic strips is the wireless link between the reader and the transceiver: the read/write unit does not require visual contact with the transceiver, so Fully integrated into the product. This means that the transceiver is suitable for harsh environments and the transceiver is not sensitive to wet, dirty and mechanical effects. Therefore, the transceiver system has very high read reliability and fast data acquisition. The last point is also important to save labor and paper.
The company adheres to the management policy of "seeking truth and dedication" and a strict quality assurance system. In the new century, we will follow the tenet of "innovation, progress and rigor" and a forge ahead enterprise with "excellent quality and excellence". Spirit, the supreme product, add wings to your enterprise take off. Carefully do a good job of each product, the highest quality, and integrate a dedicated attitude, dedicated spirit, skilled practice, and good reputation into the details of the service.
High Voltage Connector,High Voltage Terminal Wire Connectors,High Voltage Terminal Connectors,High Voltage Terminal Connector Terminal
Sichuan Xinlian electronic science and technology Company , https://www.sztmlchs.com