When we talk about driverless technology, we’re not referring to a single autonomous entity, but rather an entire system of advanced technologies working in harmony. This includes radar sensors, sophisticated algorithms, and one of the most commonly used tools—GPS. GPS plays a crucial role in ensuring that self-driving cars stay on the correct path, avoiding confusion or disorientation like a fly without a head. Let’s explore how this technology works and why it matters.
Most of us are familiar with GPS, often starting with our smartphones. It has become such a part of daily life that we rarely question how it actually functions. While we know it helps us find our way, few understand the science behind it. This lack of awareness can be concerning, especially as GPS becomes more integrated into critical systems like autonomous vehicles.
The full name of GPS is Global Positioning System, a satellite-based navigation system originally developed by the U.S. military. In the 1950s and 1960s, the Department of Defense created a network of satellites to support navigation for land, sea, and air forces. By the end of the Cold War, 24 satellites were launched, making GPS fully operational. Later, it was introduced to the civilian market, leading to widespread use and near-monopoly across the globe.
Technically, GPS operates using a method called trilateration. Satellites in orbit transmit signals to receivers on the ground. The receiver calculates its distance from each satellite based on the time it takes for the signal to travel. Using these distances and the known positions of the satellites, the system determines the exact location of the receiver on Earth.
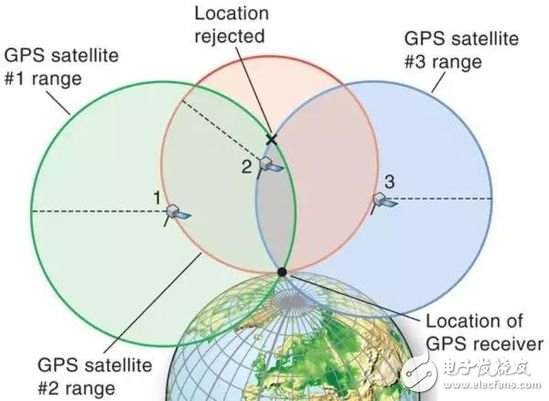
GPS You Don’t Know Can Be More Dangerous Than You Think
It's unsettling to realize that something so integral to our lives originated from the U.S. military. This raises important questions about control, security, and privacy. While GPS is convenient, it also poses risks when misused or manipulated.
Many apps and devices collect and share your location data without clear consent. For example, Uber faced backlash when users discovered that the app continued tracking their location even after a ride had ended. Such practices highlight the need for greater awareness and regulation around how our data is handled.

(The area around the Pentagon)
Smart devices, including fitness trackers, also gather location information. A recent incident involving a smart bracelet company revealed that user movement data was displayed publicly through thermal maps. This raised concerns, especially when such devices were issued to military personnel, exposing sensitive locations.
Moreover, GPS signals can be faked. Games like Pokémon Go, which rely on location-based services, have shown how easily GPS can be manipulated. With relatively inexpensive equipment, individuals can trick systems into thinking they're somewhere else, highlighting vulnerabilities in the technology.

So what does this mean for the future of driverless cars? If GPS is compromised, it could lead to serious consequences, from service disruptions to traffic accidents. As autonomous vehicles become more common, the risks associated with GPS will affect everyone, not just specific groups.
The Future of Unmanned Driving
Some may ask, “What does this have to do with me?†While it’s true that many people trade some privacy for convenience, the potential for misuse remains high. Third parties can access location data through various means, often without users' knowledge. This creates a real threat to personal privacy and security.
Imagine someone tracking your movements without your consent. It could be a partner, a parent, or even a stranger with malicious intent. These scenarios are not far-fetched and show how vulnerable we are in the digital age.

Now, consider the implications on a larger scale. If a country relies on foreign GPS systems, it could face serious disruptions during conflicts. A simple signal jamming could bring an entire autonomous transport system to a halt, or worse, cause deadly accidents.
To avoid such risks, countries like China, Russia, and the European Union have developed their own satellite navigation systems. China’s BeiDou system, for instance, now covers the globe and is playing a key role in the growth of autonomous driving in the country.
Big Country Power: Why Everyone Needs Their Own GPS?
Building a national satellite navigation system is costly, but it ensures independence and security. While GPS is widely used, relying on it leaves a country vulnerable. That’s why nations are investing in their own systems to protect critical infrastructure and maintain control over their technological future.
In the past, India faced a similar issue when the U.S. shut down GPS services during a conflict, causing significant losses. This experience led India to develop its own regional navigation system. Similar situations could happen to any country that doesn’t have control over its positioning technology.
As unmanned technology advances, it becomes increasingly dependent on satellite navigation. Without reliable systems in place, the development of autonomous vehicles could be severely limited. This makes it essential for countries to invest in and maintain their own navigation networks.
While challenges remain, such as data privacy and signal manipulation, the best approach is to stay informed. Always check app permissions, read user manuals, and remain vigilant about how your data is being used. After all, in the world of technology, awareness is the first line of defense.
HIFU Piezoelectric Ceramic Parts
High Intensity Focused Ultrasound (HIFU) technology is to focus ultrasound on a single point to produce high energy, function on the dermis and SMAS layer of skin, stimulate the proliferation and recombination of collagen, effectively achieve the effect of compact contour and smoothing lines.
Focused ultrasound does not heat the skin surface, nor does it need to pass through the skin as a medium for the transmission of laser energy, so it does not affect the tissue on the skin surface and the tissue through which the laser passes, of course, there will be no excessive heat residue on the skin surface. In this way, the epidermis will not be affected by heat, which can reduce the Eastern people's thermal reaction easily, and greatly reduce the chance of scald. Focused ultrasoundtherapy produces thermal coagulation points in the SMAS layer, and the thermal effect diffuses outward from the coagulation points, so the heat source is concentrated in the SMAS layer to be treated. It can produce more collagen denaturation.
Ultrasonic Transducer Component,Piezo Crystal For Vibration Transducer,Piezoelectric Ultrasonic Rings,High Power Ultrasonic Machining
Zibo Yuhai Electronic Ceramic Co., Ltd. , https://www.yhpiezo.com