Guide: As a critical component in the execution unit, the servo motor plays a pivotal role in determining the performance of robots. It is also considered one of the key areas where China’s robotics industry needs improvement. The “Made in China 2025†initiative has set a goal for robotic servo motors: by 2020, their performance, precision, and reliability should reach levels comparable to those of similar foreign products.
As an actuator within the control system, the servo motor is one of the three core components of a robot. The robot servo system comprises three parts: the servo motor, the servo drive, and the command mechanism. The servo motor serves as the actuator, relying on it to execute movements. The servo drive functions as the motor's power source, while the command mechanism provides pulses or speed instructions to work with the servo drive.
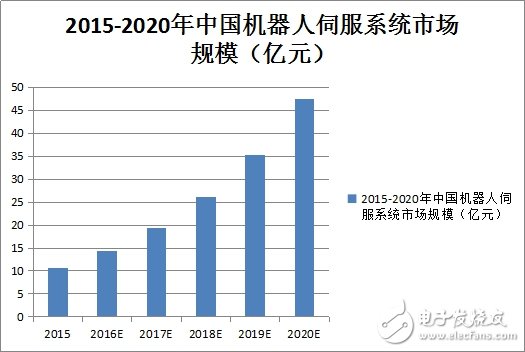
In 2015, the market size for robotic servo systems in China was approximately 1.06 billion yuan. By 2020, this figure had grown to 4.7 billion yuan, with a compound annual growth rate of around 35% expected over the next five years.
The image below illustrates the servo motor, a "weak point" that domestic robots need to address:
Both domestic and international servo system manufacturers view the robotics market as a key area for future development. Typically, servo motors are installed at the "joints" of robots, making the joint drive inseparable from the servo system. The more joints a robot has, the greater its flexibility and precision, requiring more servo motors.
The global demand for robots is expanding rapidly, with China currently being the fastest-growing robotics market in the world. From 2013 to 2016, China became the largest consumer market for industrial robots for three consecutive years. According to IDC predictions, by 2020, the Chinese robotics market will reach $59.4 billion, accounting for more than 30% of the global robotics market. This presents immense market potential. The rapid growth in robotics will drive significant demand for servo motors.
**Challenges Facing Robot Servo Motors**
Servo motors are often connected to terminal actuators in automated control systems and are thus implemented as motors. In the servo system, the servo motor functions as an actuator, converting the pulse signals from the servo controller into the angular displacement and velocity of the motor's rotation.
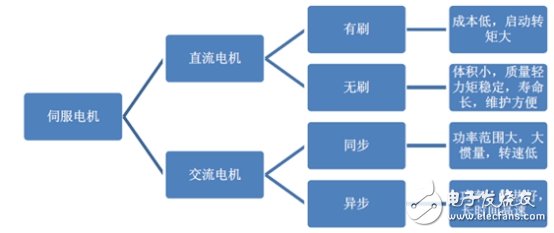
Servo motors are primarily categorized into two types: DC and AC servo motors. Compared to regular motors, their main feature is that they are typically used with feedback devices to achieve precise control.
Classification of Servo Motors:
To enhance the flexibility of industrial production, robots are becoming increasingly lightweight, necessitating high-density servo motors to ensure dynamic performance and precision. In fine machining operations, robots require the same dexterity as human hands. The motor must deliver high performance within limited dimensions, improving production quality and efficiency while ensuring operator safety. In the field of medical robots, the motor's stability and reliability are crucial to help patients recover quickly.
**High Requirements for Robots on Servo Motors**
1. The servo motor must respond quickly. The motor should transition from receiving a command signal to executing the required operation in minimal time. A shorter response time indicates higher sensitivity in the electric servo system and better fast-response capabilities. Generally, the servo motor's performance is measured by its electromechanical time constant.
2. The starting torque of the servo motor should be greater than the inertia ratio. When driving a load, the robot's servo motor requires a large starting torque and a small moment of inertia.
3. The servo motor should exhibit continuous and linear control characteristics. As the control signal changes, the motor's speed should vary continuously. Ideally, the speed should be proportional to or directly related to the control signal.
4. To match the robot's design, the servo motor must be compact in size, lightweight, and short in axial length.
5. It must withstand harsh operating conditions, including frequent forward and reverse movements, acceleration and deceleration cycles, and multiple overloads in a short period. AC servo drives are widely used in industrial robots due to their advantages of high torque-to-inertia ratios, brushless operation, and no sparking during commutation.
In conclusion, the demand for advanced servo motors is growing exponentially, driven by both technological advancements and market expansion. Addressing these challenges is vital for the continued success of robotics industries worldwide.
Ceramic Insulator,Ceramic Electrical Insulators,Ceramic Standoff Insulators,Ceramic Isolators
Yixing Guangming Special Ceramics Co.,Ltd , https://www.yxgmtc.com