The demand for meat and dairy products is continuously rising, and consumers are increasingly concerned about the safety and reliability of these food items. This growing awareness presents new challenges for businesses in the industry, requiring them to implement comprehensive management systems that strictly monitor and control the entire production and processing chain. Over the past decade, numerous animal disease outbreaks have occurred globally, such as mad cow disease, Streptococcus suis, foot-and-mouth disease, and avian flu, which not only threaten public health but also severely impact the livestock industry. As a result, governments worldwide have taken swift actions, introducing policies and measures to enhance monitoring and management of animals. Among these efforts, animal identification and tracking has become a key strategy. For instance, the British government has implemented various tracking and identification methods for animals like pigs, horses, cattle, sheep, and goats.
The main objective of this research is to develop an efficient and user-friendly management system using RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology to improve the modernization of pig farm operations. This system allows for quick tracing of pork and its products in case of issues, enabling timely identification of the source of diseases and appropriate responses to minimize losses. RFID is a non-contact automatic identification technology with advantages such as large data storage capacity, read/write functionality, strong penetration, long reading distance, fast speed, long lifespan, and good environmental adaptability. It is the only automatic identification technology capable of recognizing multiple targets simultaneously.
The RFID-based animal identification and tracking management system consists of three components: RFID tags, readers/writers, and a computer network, as illustrated in Figure 1. The reader, typically used as a computer terminal, handles data reading, writing, and storage of RFID tags. It comprises a control unit, high-frequency communication module, and antenna. This system includes both fixed and handheld readers. RFID tags are passive transponders, primarily composed of an integrated circuit (IC) chip and an external antenna. The RFID chip usually integrates RF front-end, logic control, memory, and sometimes even the antenna on the same chip.
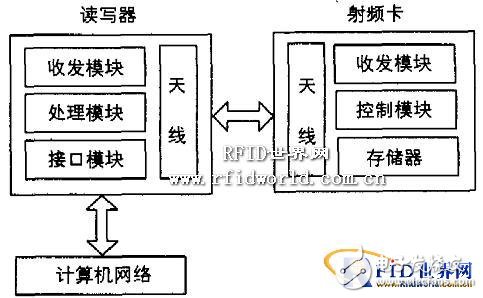
Figure 1: Structure of the RFID-based animal identification system
The basic working principle of the system involves a pig wearing an RFID tag (ear stud) entering the reader’s RF field. The antenna induces a current, which is boosted by a circuit to power the chip. The information-carrying current is detected by the RF front-end and processed by the logic control circuit. The required data is retrieved from memory and sent back through the RF front-end to the reader via the antenna. The computer network then collects this data through an interface, integrating essential functions for daily pig farm management. All records, statistics, and reports involved in daily operations are now managed digitally, improving efficiency and accuracy. This system meets current production needs and supports better decision-making for farm managers, enhancing overall management standards.
In terms of hardware design, the system includes three main parts: the installation of the RFID tag (ear stud), the implementation of the RFID reader, and the integration of the computer network. The RFID tag is installed on the pig's ear, serving as a unique identifier throughout its life cycle. The tag stores critical information such as the farm address, breed details, vaccination records, and health history, ensuring full traceability from birth to slaughter.
The RFID reader comes in two types: fixed and handheld. Fixed readers are installed at strategic locations within the pig house and transmit real-time data to the software platform via a CAN bus network. Handheld readers, on the other hand, allow users to collect large amounts of RFID data and transfer it to the PC through USB or COM ports. Both types of readers play a crucial role in ensuring accurate and efficient data collection and management.
This system not only improves operational efficiency but also enhances transparency and accountability in the livestock supply chain. By leveraging RFID technology, the system provides a reliable solution for tracking and managing animals, ultimately contributing to safer and more sustainable food production.
Naked Eye 3D Led Display,Glasses-free 3D LED display,Direct-view 3D LED display,3D LED display without glasses,Advanced naked-eye 3D LED display,Naked Eye 3D LED billboard Outdoor
Shenzhen Xinfei Century Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.rgbdancing.com