Recently, the co-founder and CTO of Mate Labs published an article on Medium titled "Everything You Need to Know About Neural Networks," covering everything from neurons to epochs, and introducing the key terminology behind neural networks. This guide aims to simplify the core concepts and provide a clear understanding for those interested in machine learning.
Understanding artificial intelligence and how machine learning and deep learning shape it is both fascinating and rewarding. At Mate Labs, we have a team of self-taught engineers who believe that sharing knowledge can help others avoid common pitfalls and accelerate their learning journey. This article is a small contribution to that mission, offering insights into some essential terms in the world of neural networks.
A **neuron** (or node) is the fundamental building block of a neural network. It receives multiple inputs, each multiplied by a corresponding weight. These weighted inputs are then summed, and an activation function is applied. For example, if a neuron has four inputs, there are four weights associated with them, which are adjusted during training to improve the model's performance.
Connections between neurons carry these weighted signals. The goal of training is to adjust these weights so that the network produces accurate outputs, minimizing the error or loss.
An **offset** (also known as a bias) is an additional input that always has a value of 1. It allows the neuron to activate even when all other inputs are zero, providing more flexibility in modeling complex patterns.
The **activation function** introduces non-linearity into the network, enabling it to learn and represent more complex relationships. Common functions include ReLU, Sigmoid, and TanH. Each has its own characteristics, and choosing the right one depends on the problem at hand.
In a basic neural network, the **input layer** receives the raw data and passes it to the next layer without any processing. The **hidden layer(s)** perform the bulk of the computation, transforming the input through a series of weighted sums and activation functions. The final **output layer** produces the predicted result, such as class labels or numerical values.
The **input shape** refers to the dimensions of the data being fed into the network. For instance, if you're working with a single sample containing four features, the input shape would be (1, 4, 1). If you have 100 samples, it becomes (100, 4, 1).
**Weights** determine the influence of each input on the output. Larger weights indicate stronger connections, while smaller or negative weights suggest weaker or inverse effects. Adjusting these weights during training is crucial for the network to make accurate predictions.
**Forward propagation** is the process of passing input data through the network layer by layer, applying weights, biases, and activation functions to generate an output. This is also referred to as inference, where the model uses what it has learned to make predictions based on new data.
By understanding these fundamental components, learners can build a solid foundation in neural networks and better navigate the complexities of deep learning. Whether you're just starting out or looking to deepen your knowledge, this guide offers a clear path to mastering the essentials.
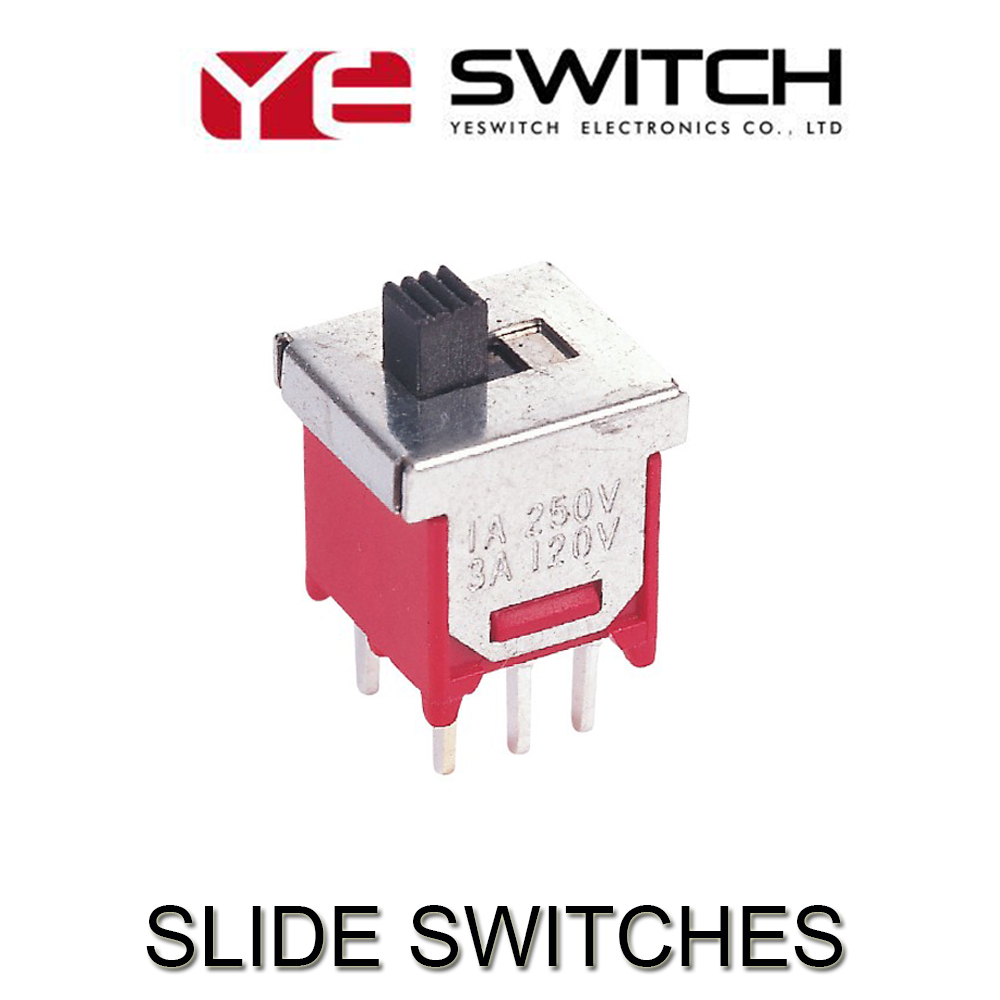
Slide Switch
Slide Switches
The Slide Switches is used to switch the circuit by turning the switch handle to turn the circuit on or off. It is different from our other serious switches, for example, Metal Switches, Automotive Switches, LED light Switches, Push button Switches, Micro Switches, The commonly used varieties of Miniature Slide Switches are single pole double position, single pole three position, double pole double position and bipolar three position. It is generally used for low voltage circuits, featuring flexible slider action, stable and reliable performance. Mainly used in a wide range of instruments, fax machines, audio equipment, medical equipment, beauty equipment, and other electronic products.
The Mini Slide Switches are divided into: low-current slide switches (right), and high-current slide switches (left). Small current slide switches are commonly used in electronic toys, digital communications. High current is generally used in electrical appliances, machinery, etc.

It can divided into 4 types modals, respectively are:
1. High-current sealed switch
Its rated current is as high as 5A, and it is sealed with epoxy resin. It is a large current sealed switch. It has a variety of terminal forms, contact materials are silver, gold, switching functions. Therefore, there are many types of subdivisions. Widely used in electrical appliances and machinery
2. Single sided snap-on surface mount type slide switch
The actuator is operated on the side and the pins are patch-type, so it is a unilateral spring-back surface mount type slide switch. Widely used in communications, digital audio and video
3.4P3T in-line slide switch
The contact form is 4P3T and the pin is in-line. It is 4P3T in-line slide switch. 4P3T determines that it has 8 pairs of pins. At the same time, there are two pairs of brackets that support, fix, and ground. Widely used in building automation, electronic products
4.Long actuator jacking type slide switch
Actuator 12mm, and located at the top of the switch, it is a long actuator jacking type slide switch. Widely used in digital audio and video, various instruments / instrumentation equipment
Slide Switches,Micro Slide Switch,2 Position Slide Switch,Momentary Slide Switch
YESWITCH ELECTRONICS CO., LTD. , https://www.yeswitches.com

